A range of teacher professional learning programs will be developed to accompany the Biodiversity of the Western Volcanic Plains online outreach...
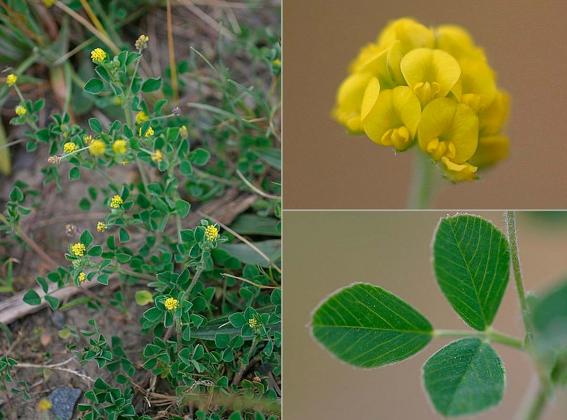

Suckling Clover
Trifolium dubium
Annual. Many species of clover are cultivated as pasture plants and readily spread to disturbed sites including roadsides and paddocks.
| Details | Description |
| Type | Herb |
| Group | Pea |
| Identifying Characteristics | |
| Distinctive Features | The inflorescence is hemispherical. |
| Life Form Group | Herb |
| Life Form Codes | Medium Herb (MH) |
| EVC types | EVC 132_61: Heavier-soils Plains Grassland EVC 132_62: Lighter-soils Plains Grassland EVC 132_63: Low-rainfall Plains Grassland EVC 803: Plains Woodland |
| Native Status | Introduced |
| Weed Status Invasiveness | High INVASIVE |
| Weed Status Impact | Low IMPACT |
| Taxonomy | |
| Phylum | Charophyta |
| Class | Equisetopsida |
| Order | Fabales |
| Family | Fabaceae |
| Genus | Trifolium |
| Species | dubium |
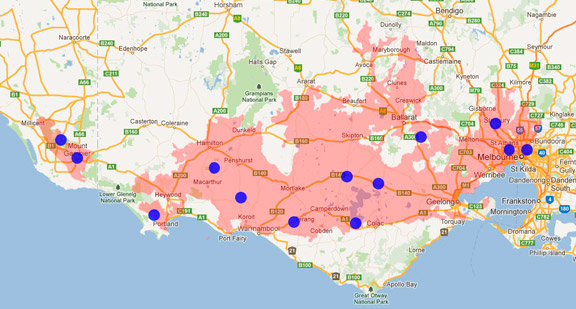
Distribution maps indicate current and historic locations where species have been sighted.
Source: Atlas of Living Australia
| Endangered Status | |
| DEPI Advisory List | Not listed |
| FFG Act | Not listed |
| EPBC Act | Not listed |
The conservation status of species is listed within Victoria and Australia.
The Department of Environment and Primary Industry (DEPI) Advisory List consists of non-statutory advisory lists of rare or threatened flora and fauna within Victoria.
The Flora and Fauna Guarantee Act 1988 (FFG Act) lists threatened species in Victoria. Under the Act, an Action Statement is produced for each listed species.
The Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999 (EPBC Act) is the Australian Government’s key piece of environmental legislation, listing nationally threatened native species and ecological communities.