A range of teacher professional learning programs will be developed to accompany the Biodiversity of the Western Volcanic Plains online outreach...



Tiger Snake
Notechis scutatus
Viviparous (live young). Producing 20-30 live young late summer or early autumn. Active day and night.
| Details | Description |
| Type | Reptile |
| Group | Snake |
| Other Common Names | Mainland Tiger Snake |
| Identifying Characteristics | |
| Distinctive Markings | Alternating light and dark bands. Occasionally bands may be absent |
| Diet | Carnivore. Frogs and small insects including cicadas, moths and caterpillars. |
| Habitat | Prefers swampy or marshy ground. Found near creeks, rivers or dams. |
| Native Status | Native to Australia |
| Taxonomy | |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Class | Reptilia |
| Order | Squamata |
| Family | Elapidae |
| Genus | Notechis |
| Species | scutatus |
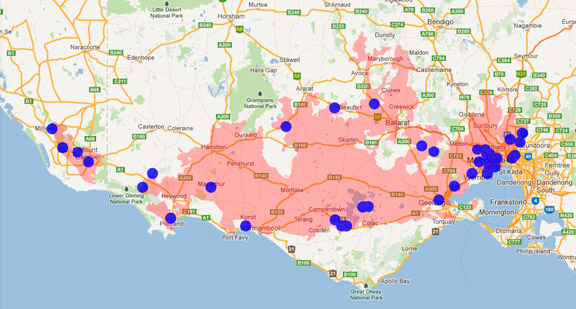
Distribution maps indicate current and historic locations where species have been sighted.
Source: Atlas of Living Australia
| Conservation Status | |
| DEPI Advisory List | Not listed |
| FFG Act | Not listed |
| EPBC Act | Not listed |
The conservation status of species is listed within Victoria and Australia.
The Department of Environment and Primary Industry (DEPI) Advisory List consists of non-statutory advisory lists of rare or threatened flora and fauna within Victoria.
The Flora and Fauna Guarantee Act 1988 (FFG Act) lists threatened species in Victoria. Under the Act, an Action Statement is produced for each listed species.
The Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999 (EPBC Act) is the Australian Government’s key piece of environmental legislation, listing nationally threatened native species and ecological communities.