A range of teacher professional learning programs will be developed to accompany the Biodiversity of the Western Volcanic Plains online outreach...
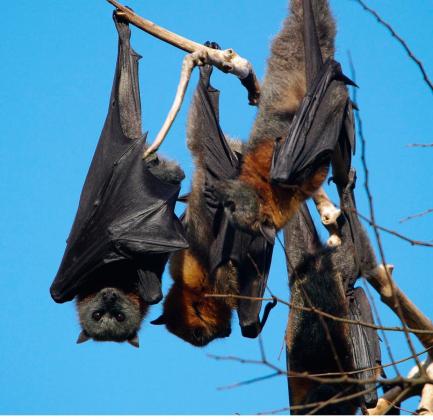
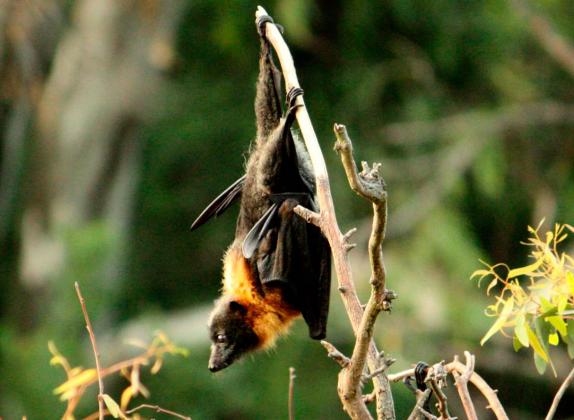


Grey-headed Flying Fox
Pteropus poliocephalus
Nocturnal. During the day large groups roost in branches of large trees where they sleep hanging upside down. Some roosting sites appear to have been regularly used by the Grey-headed Flying Fox since before European settlement.
| Details | Description |
| Type | Mammal |
| Group | Placental |
| Other Common Names | Grey-headed Fruit-bat |
| Identifying Characteristics | |
| Distinctive Markings | Grey or brown fur with orange fur around neck. |
| Diet | Herbivore. Natural food preferences are native fruits and the blossom and nectar of eucalypts, but also feeds on the fruits and flowers of introduced trees in gardens and orchards. |
| Habitat | Lowland and coastal forests and woodlands, agricultural and urban areas. |
| Native Status | Native to Australia |
| Sounds | Screeches and squeals. |
| Taxonomy | |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Class | Mammalia |
| Order | Chiroptera |
| Family | Pteropodidae |
| Genus | Pteropus |
| Species | poliocephalus |
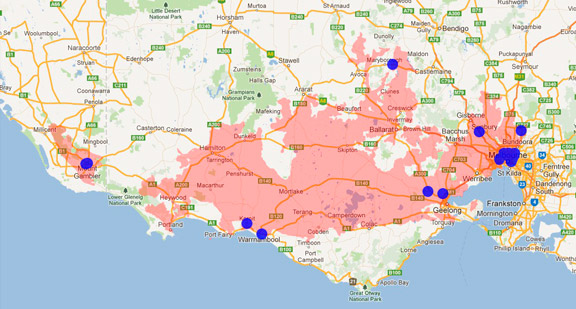
Distribution maps indicate current and historic locations where species have been sighted.
Source: Atlas of Living Australia
| Conservation Status | |
| DEPI Advisory List | Vulnerable |
| FFG Act | Listed as threatened |
| EPBC Act | Vulnerable |
The conservation status of species is listed within Victoria and Australia.
The Department of Environment and Primary Industry (DEPI) Advisory List consists of non-statutory advisory lists of rare or threatened flora and fauna within Victoria.
The Flora and Fauna Guarantee Act 1988 (FFG Act) lists threatened species in Victoria. Under the Act, an Action Statement is produced for each listed species.
The Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999 (EPBC Act) is the Australian Government’s key piece of environmental legislation, listing nationally threatened native species and ecological communities.